
She is a freelance horn player in the Bay Area. She has degrees in Horn Performance from the University of the Pacific Conservatory of Music and the University of North Carolina at Greensboro. Jacy Burroughs is the Assistant E-Commerce Marketing Manager at Sheet Music Plus. He died exactly one month later, on Apat the age of 63. The piece received a standing ovation after each movement. His last public appearance was on Maat the performance of his Symphony No. Who was Johannes Brahms Ivan Hewett, Bayan Northcott and Jessica Duchen take a look at the essence of this enigmatic composer. 115, two clarinet sonatas, several song cycles for piano and the Eleven Chorale Preludes for Organ Op. However, he was unable to maintain his resolve because he ended up composing his Clarinet Trio Op. In 1890 at the age of 57, Brahms decided to give up composing. Arguably his most massive piece and the work that put him on the map was his German Requiem, composed the year after his mother died.ĩ.

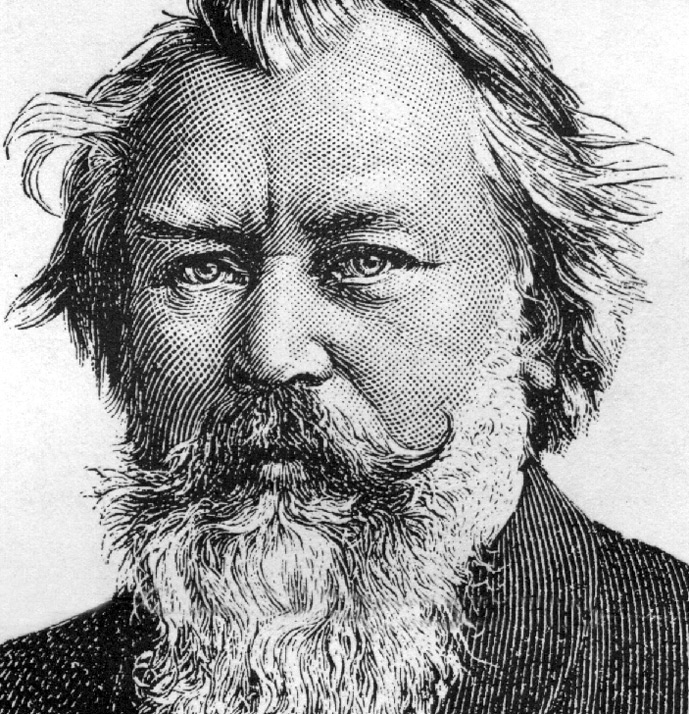
He wrote over 200 lieder, several piano sonatas and chamber works for various string ensembles. He wrote several major works for orchestra including four symphonies, two serenades, two piano concertos, a violin concerto, the Academic Festival Overture and the Tragic Overture. While his compositional output was not nearly as numerous as Mozart’s or Beethoven’s, it was significant. He was briefly engaged in 1859 to an Agathe von Siebold, who broke off the engagement.Ĩ. Even after Robert Schumann’s tragic death in 1856, Clara and Brahms remained only friends. However, it is unclear whether the feeling was mutual. Music historians believe that Brahms was in love with Clara Schumann. Conductor and virtuoso pianist Hans von Bulow once called Brahms’ Symphony No. The conservatives believed that Beethoven’s greatness could not be surpassed the progressives believed his music was the start of a new era.Ħ. Both groups believed they were in the musical lineage of Beethoven. This conflict came to be known as the War of the Romantics. Their opponents, musical conservatives like Brahms and Joseph Joachim, found this music to be over-dramatic they were proponents of absolute music – music that is non-representational or not specifically about anything.ĥ. The New German School pushed the boundaries on chromatic harmony, musical structure and advocated for program music (music that has extra-musical meaning it is meant to depict a story or narrative). Schumann was so impressed with Brahms’ compositions that he wrote an article in his Neue Zeitschrift f ü r Musik, praising the young composer’s genius and heralding him as the one who could overthrow the New German School of Liszt and Wagner.Ĥ. He did not become famous as a composer until April and May of 1853, when he was on a concert tour as accompanist to the Hungarian violinist Eduard Reményi.ģ. Brahms is also believed to have begun composing early in his life, but destroyed his early compositions. By the time he was a teenager, he was helping the family financially by performing in inns, brothels, taverns and along the city docks. Brahms began playing piano at the age of 7.
#Brahms compositions professional#
Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. His father was a town musician who played a variety of instruments, mostly horn and double bass.Ģ. Johannes Brahms was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid-Romantic period.

In 1971, Håkon he won the prestigious Olivier Messiaen prize.1. Håkon Austbo was born in Norway, and now resides on Holland. He helped establish the forms and styles for the string quartet and the symphony.
#Brahms compositions full#
Brahms was madly in love with her, but although they were great friends, his love went unrequited. Joseph Haydn, in full Franz Joseph Haydn, (born March 31, 1732, Rohrau, Austriadied May 31, 1809, Vienna), Austrian composer who was one of the most important figures in the development of the Classical style in music during the 18th century. 119 contains a Rhapsody, which is widely regarded as a final tribute to his pianist friend Clara Schumann.

118 contains severe technical demands for the performer, as well as music of incredible passion and sadness. The 3 Intermezzi are reflective, deeply personal works. 117 contains probably some of the most beautiful music Brahms’s composed. 116 set is remarkable in that its seven linked numbers form a single unity. These works are contemplative and autumnal, though the drama and tensions of the earlier works are never far away. Brahms never revisited the piano sonata form after these early works, and his output for solo piano falls distinctly into three groups: The early impetuous works, then, from 1854-73, the more technical works, and finally, the late works from the 1890s included on this CD. 1-3 typify the highly virtuosic muscular style that suited his performing style. Brahms was a formidable pianist, and his early works were written to show off his tremendous technique.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
